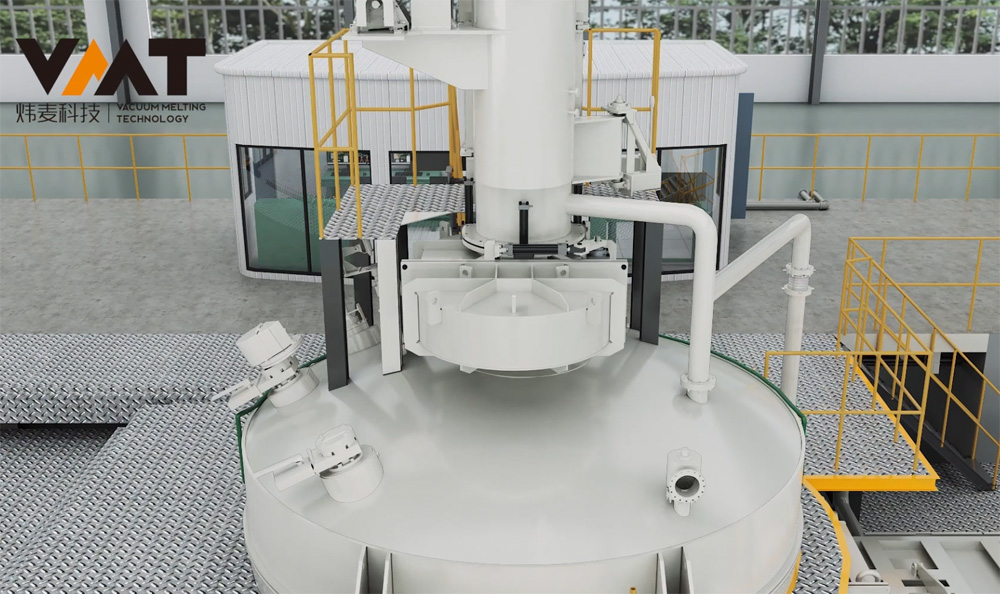
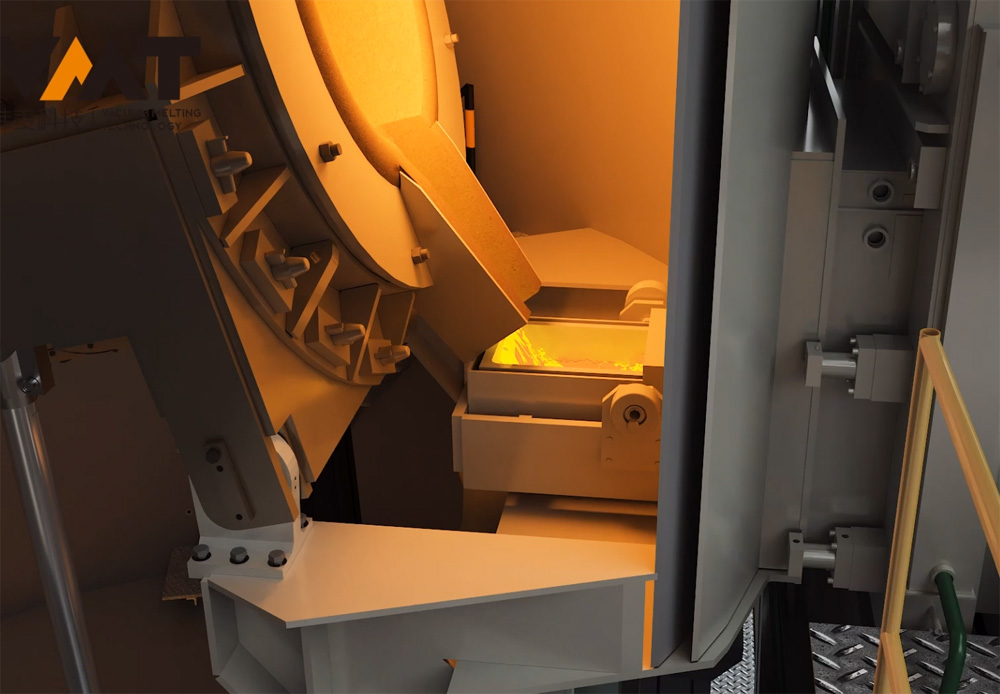
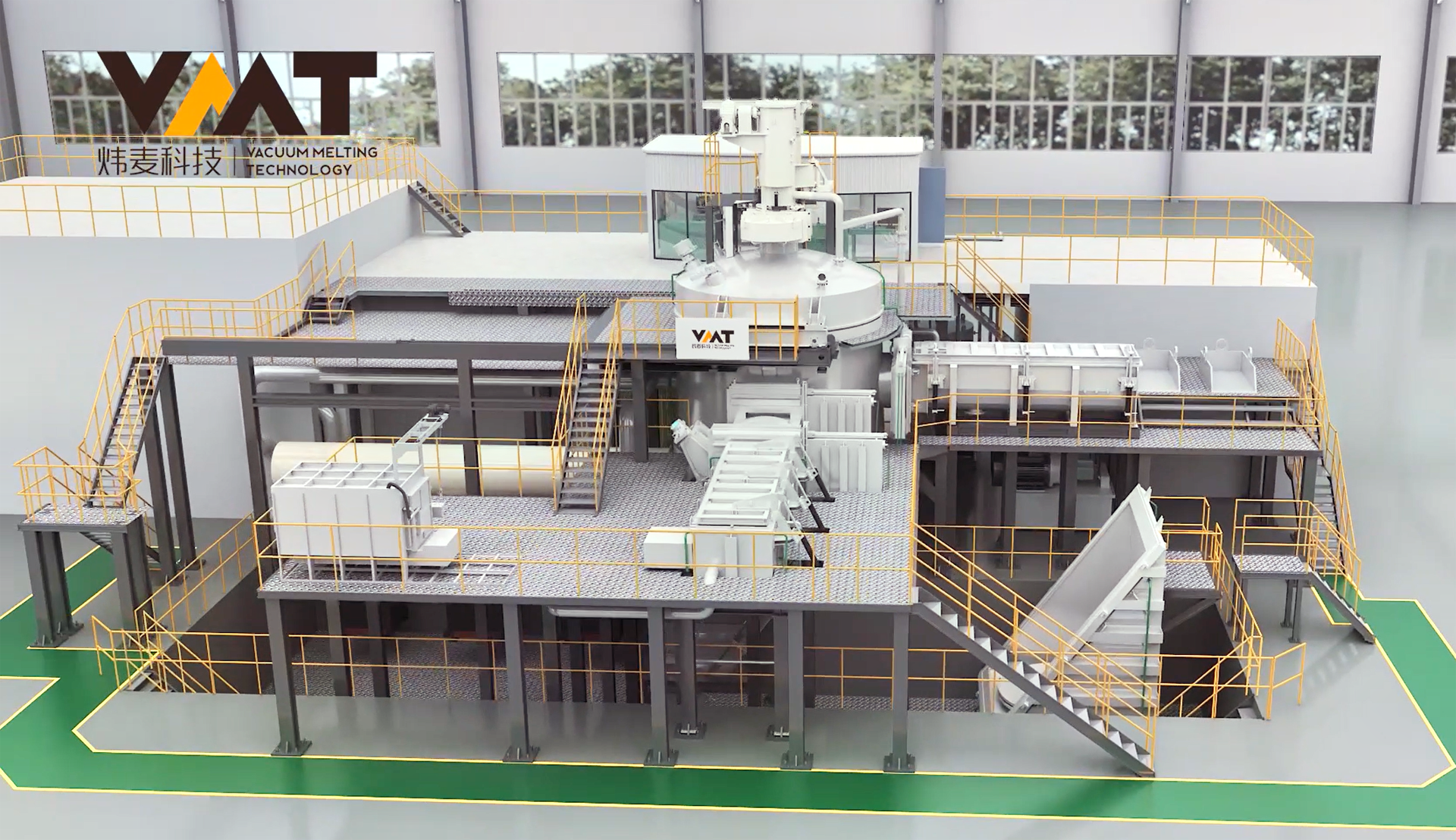
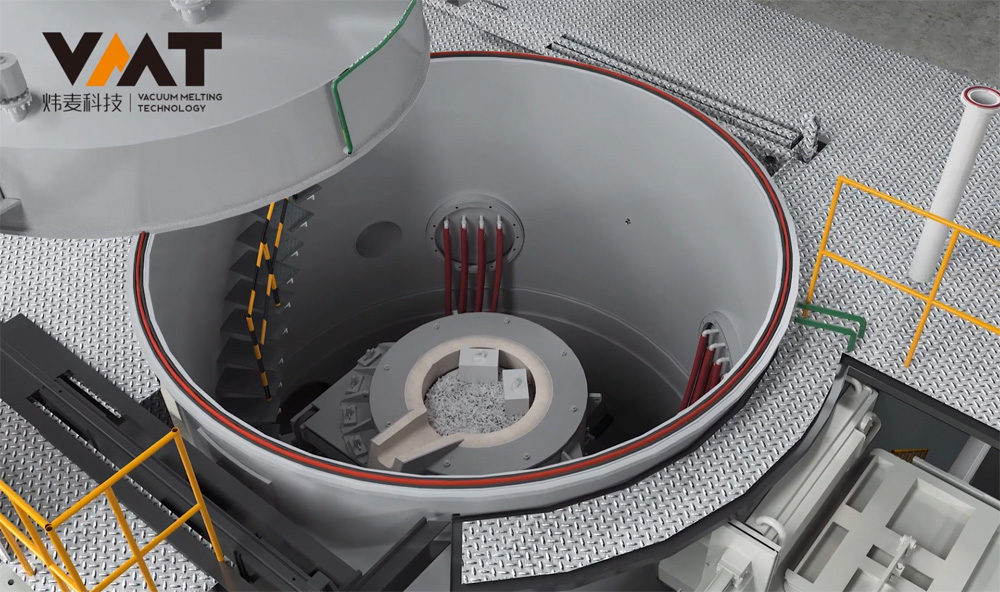
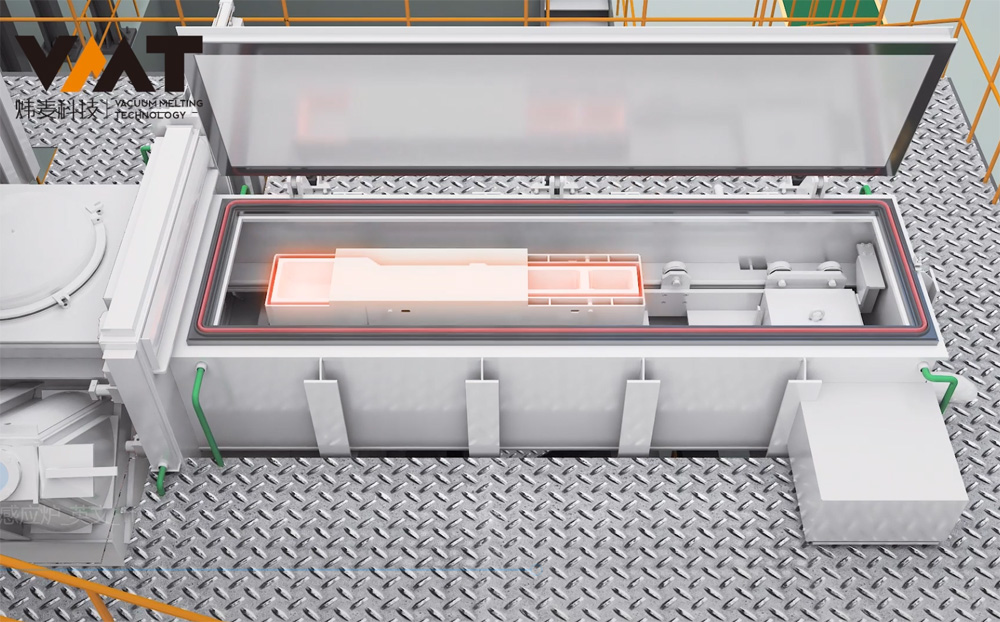
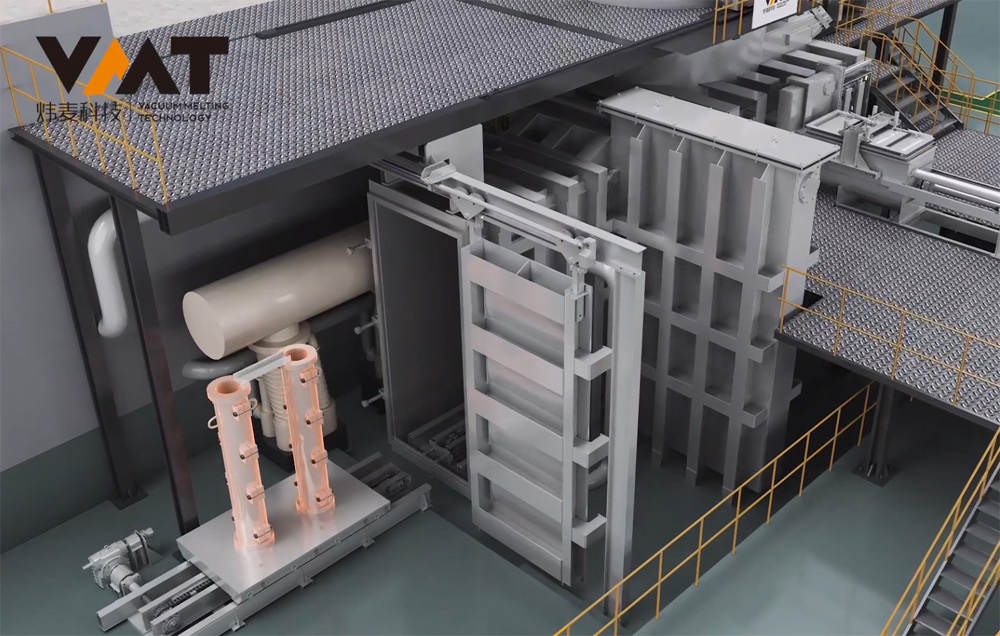
Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace (VIM) is a complete set of vacuum equipment for melting metals under vacuum conditions using medium frequency induction heating principle. VIM furnaces typically consist of parts such as melting chamber, ingot chamber, overmelt charger, side charger, tundish chamber, isolation valve, induction melting power supply, three-phase AC stirring power supply, induction furnace body, vacuum system, hydraulic system, closed cooling water system, compressed air system, argon gas system, and conductive short net, which can be modularly designed according to different customer requirements. The induction furnace body is located inside the vacuum melting chamber, with a crucible made of refractory material inside the induction furnace body, and the induction coil is outside the refractory material crucible. The induction coil has undergone special insulation and heat resistance treatment before use, avoiding arcing phenomena of the coil under vacuum. The induction furnace body is connected to the medium frequency induction power supply by a coaxial water-cooled cable, and the steel liquid melting rate is closely related to the tonnage of the furnace body, the type of metal material, and the output power of the power supply.
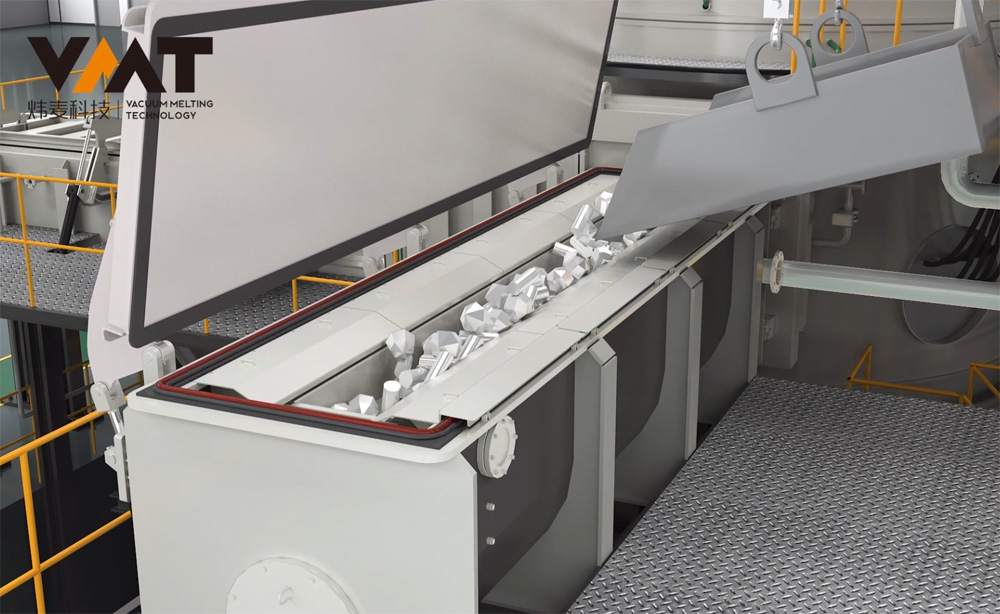
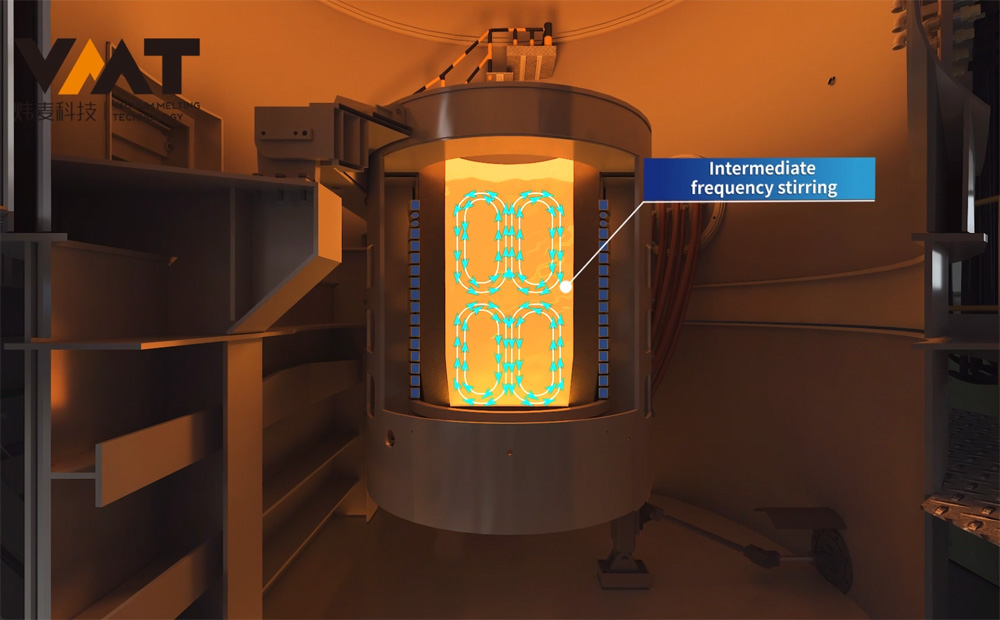
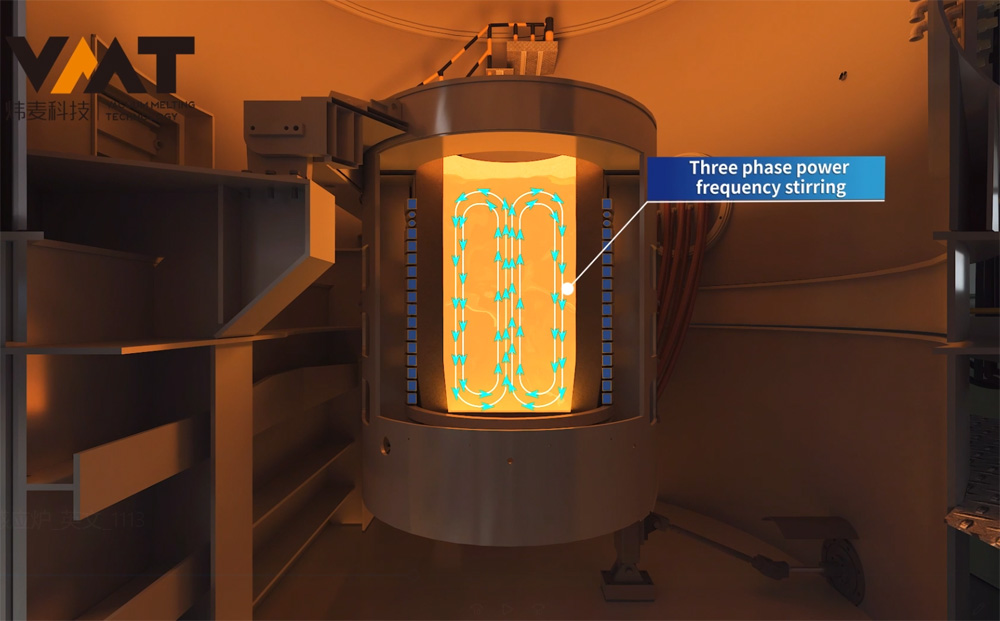
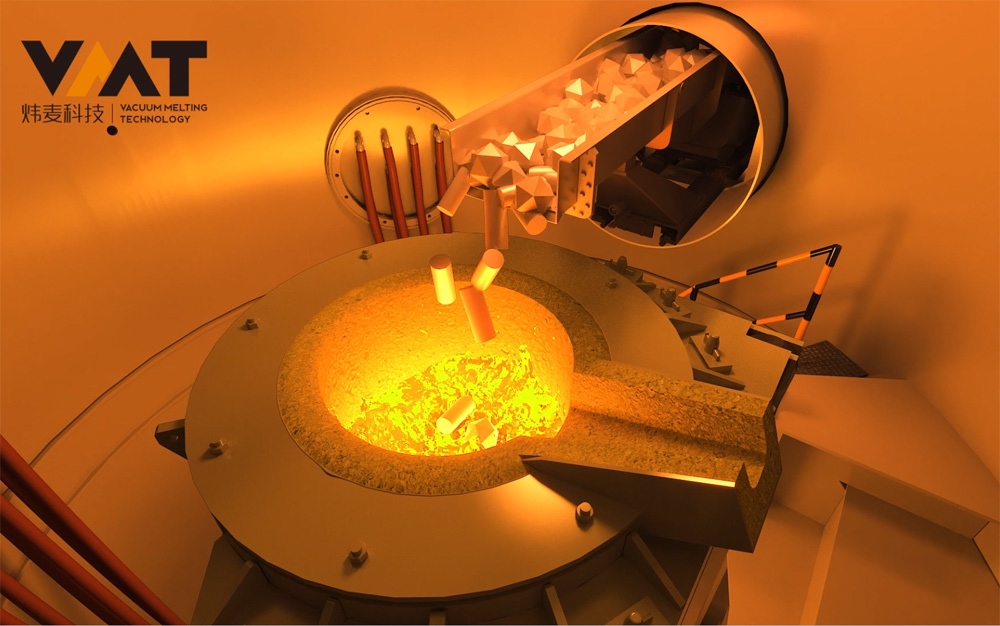
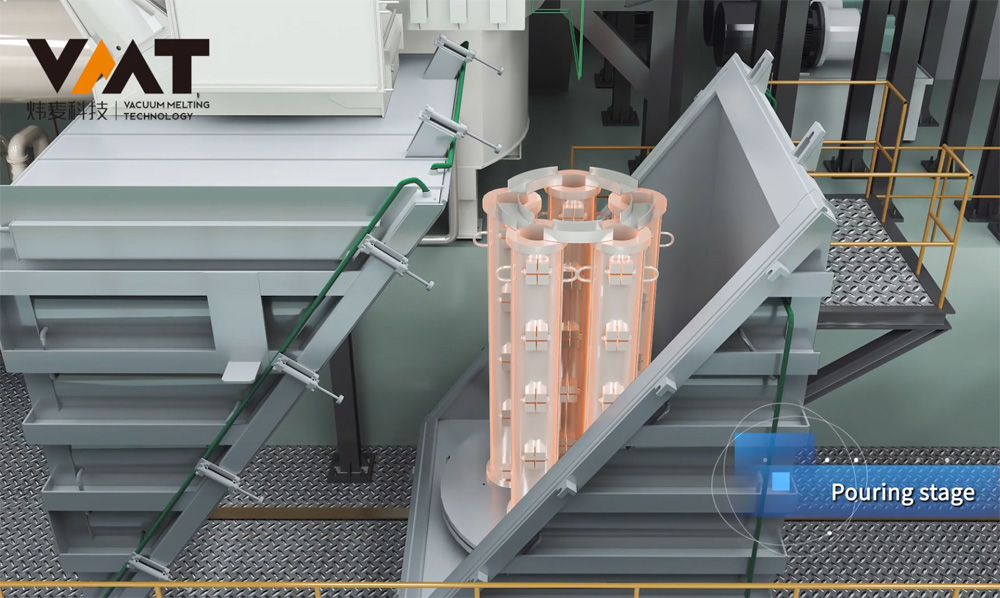
Before the cold start of VIM furnace, the operator first uses a crane to hoist the raw materials into the induction crucible, then hoists the uncharged raw materials to the positions of the side and overmelt chargers, closes the chambers, and starts the vacuum pump group of the melting chamber to evacuate. After the vacuum degree of the melting chamber reaches the process requirements, the operator starts the melting power supply and adjusts the power input according to the process requirements. When the raw materials in the induction crucible are partially melted and the upper part of the crucible is cleared, the operator continues to add materials to the induction crucible through the side and overmelt chargers in multiple batches until the raw materials reach the specified weight according to the process. After all the raw materials in the induction crucible are completely melted, the production process enters the refining period. During the refining period, the operator needs to perform operations and confirmations such as temperature measurement, sampling, alloying, and degassing of the steel liquid. To make the alloy composition more uniform and degassing more thorough during the refining period, it is necessary to start the three-phase AC stirring power supply or two-phase single-direction medium frequency stirring to fully stir the steel liquid until the final sampling (steel liquid) is qualified, and then the final pouring and molding can be carried out.
VIM furnaces can be divided into high-temperature master alloy melting furnaces and high-temperature deformation alloy melting furnaces according to the type of material melting. High-temperature master alloy melting furnaces are mainly used for producing high-temperature master alloy small rod materials for vacuum precision casting (usually the rod height is ≦1,200mm, diameter ≦120mm), and high-temperature deformation alloy melting furnaces are mainly used for remelting furnaces to produce long electrode rod materials (usually the rod height is ≦4,500mm, diameter ≦1,000mm). According to the production method, they can be divided into periodic melting furnaces and semi-continuous melting furnaces. Periodic melting furnaces are mainly suitable for pilot production lines or experimental lines, while semi-continuous melting furnaces are mainly suitable for large-scale production in factories.
Vacuum induction melting furnaces are complete sets of vacuum metallurgical equipment used for producing high-temperature alloys, ultra-high-strength stainless steels, corrosion-resistant alloys, aviation bearing steels, and other high-value special alloys.
| 0.5T | 1.5T | 3T | 6T | 8T | 12T | 20T | 24T | 30T | |
| Furnace type | periodic furnace | Semi-continuous furnace type | |||||||
| Pouring weight (nickel-based alloy) |
0.5T | 1.5T | 3T | 6T | 8T | 12T | 20T | 24T | 30T |
| Smelting chamber structure | side door | Side opening or top opening cover | |||||||
| Mold drive method | Model car drive | Mold car drive or mold plate drive | |||||||
| Feeding method | Adding ingredients | Top loading and/or side loading | |||||||
| Standard melting power | 350KW | 500KW | 750KW | 1750KW | 2000KW | 3000KW | 3500KW | 4000KW | 5000KW |